Ethical Treatments & Transparent Pricing
Welcome to the world of ethical treatments. In Parihar IVF, we are providing ethical treatments with transparent pricing. No hidden charges are in your treatment.
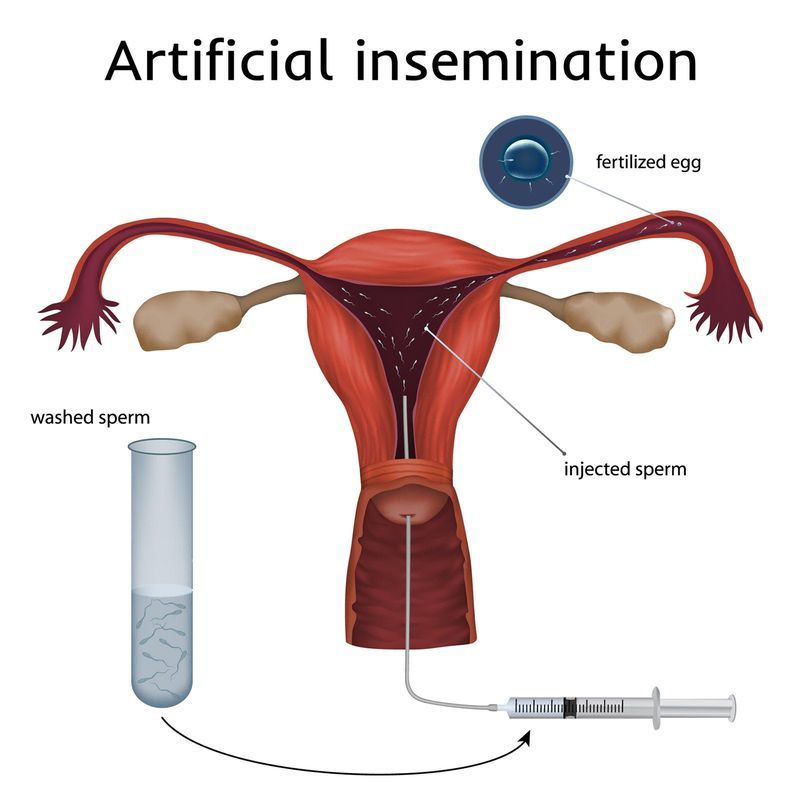
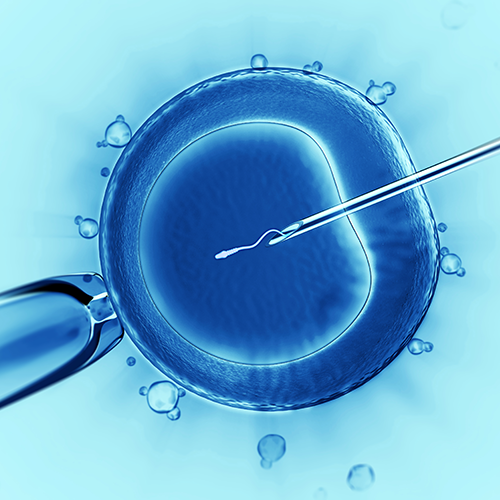
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF-ET) is popularly called test tube baby procedure. In-Vitro Fertilization means that fertilization of the egg with the sperm is established outside the body.
So in any couple where eggs are withdrawn from the ovaries and are made to fertilize using husband’s sperm outside the body and the embryo thus formed is transferred back to the uterus, the couple is said to undergo IVF procedure. It was first utilized for a couple where the woman had lost her fallopian tubes due to previous ectopic pregnancy.
Now, the indications for doing IVF are very diverse and millions of people have been helped with this technology.

Cryopreservation is a process where cells or whole “tissuesare preserved by cooling to low sub-zero temperatures, such as (typically) 77 K or −196 °C (the boiling point of liquid nitrogen.
At these low temperatures, any biological activity, including the biochemical reactions that would lead to ,is effectively stopped. However when cryoprotectant solutions are not used, the cells being preserved are often damaged due to freezing during the approach to low temperatures or warming to room temperature.





Welcome to the world of ethical treatments. In Parihar IVF, we are providing ethical treatments with transparent pricing. No hidden charges are in your treatment.
Dr. Parihar
Parihar Hospital and Fertility Center,
Opp Prem Nagar, Foy Sagar Road,
Ajmer, Rajasthan, Pin – 305001
Mob: +91-7073513498
Email: pariharhospital@yahoo.com